1 Introduction
With the growing demand of business for tighter communication and collaboration with external parties such as business partners and customers, IT has to provide the technical foundation for such integration. Web Access Management and Identity Federation are critical technologies for that evolution. They enable organizations to manage access both from and to external systems, including cloud services, in a consistent way. Organizations have to move forward towards strategic approaches to enabling that integration, in support of the Connected and Intelligent Enterprise.
While Web Access Management technologies are well established, and Identity Federation has also been around for years; we have observed tremendous growth in interest and adoption of these technologies over the past years. Customers – and specifically their business departments – are requesting solutions for emerging business requirements such as the onboarding of business partners, customer access to services, access to cloud services, and many more. IT has to react and create a standard infrastructure for dealing with all the different requirements of communication and collaboration in the Extended and Connected Enterprise. In consequence, Access Management and Federation are moving from tactical IT challenges towards strategic infrastructure elements that enable business agility.
There are many vendors in that market segment. Most of them provide solutions for both Web Access Management and Identity Federation. The major players in that market segment are covered within this KuppingerCole Leadership Compass.
This Leadership Compass provides an overview and analysis of the Web Access Management and Identity Federation market segment, sometimes referred to as Access Management/Federation. The sole focus is on solutions that are available on premises, even while we consider the fact that several of these solutions also are offered as cloud services. This can be valuable to customers if they want to start on-premises and gradually move to the cloud.
Technologies typically support both Web Access Management as a gateway approach, sitting in front of standard applications and doing authentication and authorization for backend applications, and Identity Federation. Identity Federation is strategically the more important concept; however, support of existing applications frequently favors the use of traditional Web Access Management. In addition, some Access Management solutions add features such as self-registration of users. Others also add Reverse Proxy capabilities and, based on this, Web Application Firewall functionality, which we consider as an important and valuable add-on to the core features in-scope of this document.
Overall, the breadth of functionality is increasing. Support for social logins such as Facebook or Google+, standard support for established Cloud Service Providers, and the support for new federation and related standards such as OAuth 2.0, OpenID Connect or UMA are just some of the examples for features increasingly common for this type of product.
The entire market segment is relatively mature but still evolving, and we expect to see more changes within the next few years. However, given the surging demand of businesses, organizations now have to start with implementing a standard infrastructure for (Web) Access Management and Federation. This KuppingerCole Leadership Compass provides an overview of the leading vendors in that market segment.
Besides the established vendors providing complete IAM (Identity and Access Management) product portfolios, there are some smaller vendors with interesting offerings and also specialists that purely focus on that part of the overall IAM (Identity and Access Management) market.
Picking solutions always require a thorough analysis of customer requirements and a comparison with product features. Leadership does not always mean that a product is the best fit for a particular customer and their requirements. However, this Leadership Compass will help with identifying those vendors that customers should look at more closely.
1.1 Market Segment
Access Management and Identity Federation are frequently still seen as separate segments in the IT market. However, when looking at the business problems to be solved, these technologies are inseparable. The business challenge to solve is how to support the growing “Connected and Intelligent Enterprise”. Business demands support for business processes incorporating external partners and customers. They demand access to external systems and rapid onboarding of externals for controlled and compliant access to internal systems. They request access to external services such as Cloud services, as well as capabilities to use their acquired access data to drive intelligence within their systems. The use of mobile devices is also leveraged onto organizations as the changing workforce desires to work anywhere from any device. IT has to provide an infrastructure for this increasingly connected and intelligent enterprise, both for incoming and outgoing access; both for customers and other externals such as business partners; as well as for existing and new on-premise applications, cloud services, and mobile devices.
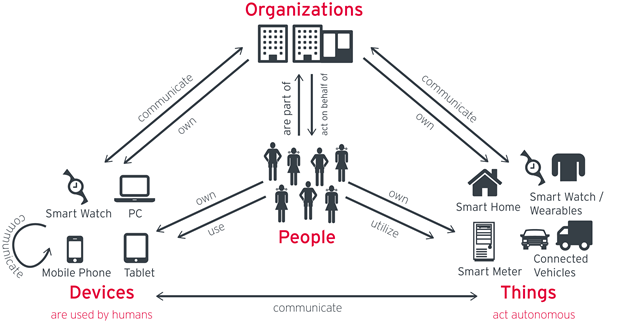
Various drivers have led to this situation. At the core is the need for agility in a complex competitive landscape. Business models have to adapt more rapidly than ever before. Supply chains include more suppliers and become increasingly more complex, with reduced vertical integration in manufacturing. Organizations also need to react more rapidly to new attack vectors that are continually changing. Customers today expect vendor’s systems to provide the intelligent access capabilities needed to combat these new threats than ever before. The changing workforce is also changing the idea that access to an organization’s resources can only be performed on-premises breaking down the traditional perimeter model. While organizations always had challenges of their changing IT environments, the density and pace of change has increased as well as the need for IT support of a more Connected and Intelligent Enterprise.
All of these trends affect today’s IT - the Computing Troika of Cloud, Mobile, Social and Intelligent Computing- stand for a shift towards an open, integrated enterprise that extend beyond the perimeter of the organization itself. Whether you tend to name this the Connected Enterprise or opt for Intelligent Enterprise does not matter. It is about the need for connecting and intelligently adapting today’s on-premise IT with the outer world in various ways.
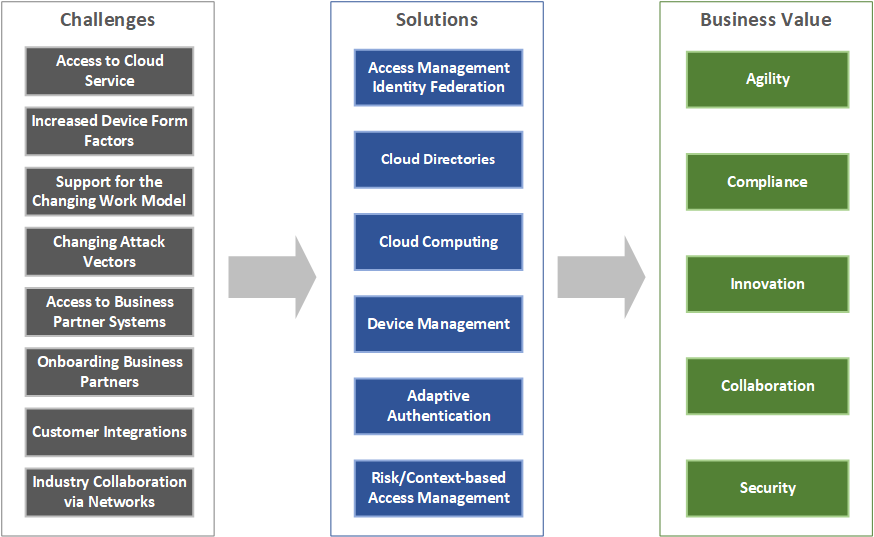
Various technologies support all the different requirements customers are facing today. The requirements are:
- Use Cloud Services: Enabling an organization to flexibly use cloud services, with maximum control of the internal and external identities using this service and the access rights they have.
- Device Form Factors: Support for the increasing number of different device form factors used in the enterprise, including desktops, tablets, mobile phones, and IoT devices.
- Access Business Partner Systems: Enable your employees to have controlled access to business partner systems with flexible onboarding and full compliance; ensure that you meet the liability agreements etc. that you have with your business partners.
- Collaborate in Industry Networks: Participate in industry networks such as healthcare professional networks, allowing the re-use of identities on such networks and the controlled access by your employees to the network as well as by network members to your systems.
- Support new Working Models: Support new working models with freelancers, mobile workers, and other forms of collaboration that allow them to work from anywhere using any device.
- Changing Attack Vectors: Provide IT security solutions that can quickly adapt and react to new forms of attacks using intelligent access controls.
- Onboarding of Business Partners: Allow your business partners to flexibly access your systems in a controlled, compliant way.
- Customer Interaction: Integrate your customers, support different types of identities such as social logins and self-registered identities, and extend your business processes to the customer.
Enabling this shift in IT from the traditional, internal-facing approach towards an open IT infrastructure supporting the Connected and Intelligent Enterprise requires various new technologies. Amongst these technologies are new types of cloud-based directory services, various other types of Cloud services including Cloud Identity Services, and improved technologies for authentication and authorization, such as risk- and context-based Access Management, also sometimes called “adaptive” authentication and authorization. However, the foundation is Access Management and Identity Federation which allows managing access to applications.
(Web) Access Management is a rather traditional approach that puts a layer in front of web applications that takes over authentication and – usually coarse-grained – authorization management. That type of application also can provide services such as HTTP header injection to add authorization information to the HTTP header that is then used by the backend application. Tools are increasingly supporting APIs for authorization calls to the system.
Identity Federation, on the other hand, allows splitting authentication and authorization between an IdP (Identity Provider) and a Service Provider (SP) or Relying Party (RP). The communication is based on protocols. Backends need to be enabled for Identity Federation in one way or another, sometimes by using the Web Access Management tool as the interface. Identity Federation can be used in various configurations, including federating from internal directories and authentication services to Cloud Service Providers or between different organizations.
Thus, these services are the foundation for enabling the various customer requirements mentioned above – enabling the Connected and Intelligent Enterprise without support for Access Management/Federation will not work.
In other words: These technologies are enabling technologies for business requirements such as agility, compliance, innovation (for instance by allowing new forms of collaboration in industry networks or by adding more flexibility in the R&D supply chain), and the underlying collaboration & communication.
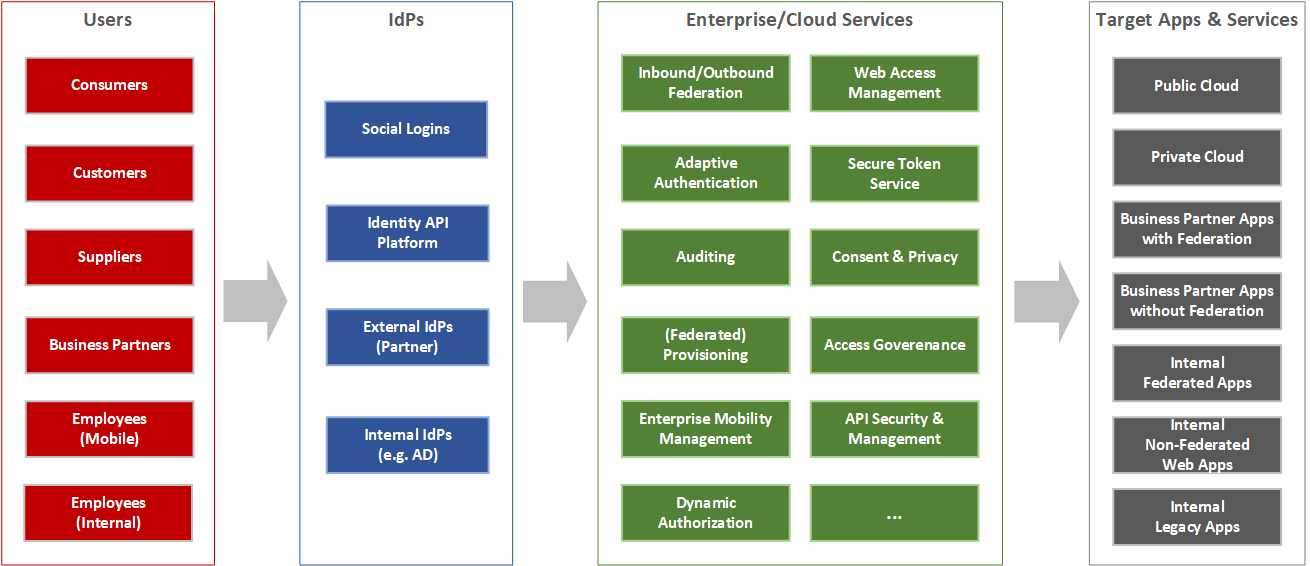
The Connected Enterprise means that organizations have to deal with more and larger user populations than ever before. Beyond the employees and some externals that have been so far managed in internal systems, more business partners, customers, and even potential customers are being added. They require access to systems, either on-premise or in the cloud. While some of the digital identities representing these persons are managed in the organization’s internal directories, others will be federated in from external Identity Providers or managed by employing Cloud Directories.
Thus, especially Identity Federation is a technology that is essential for any organization. It allows the enterprise to deal with the external identities and all the different user populations.
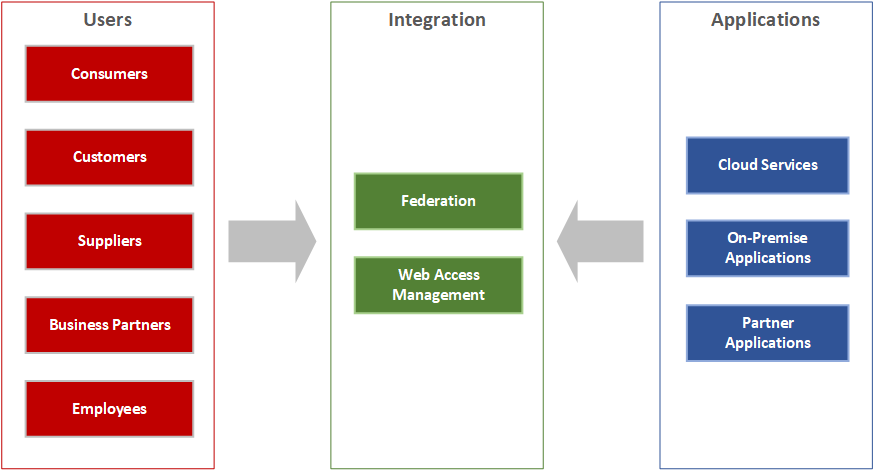
Web Access Management, on the other hand, comes into play when managing access to on-premise applications that do not support Identity Federation. While some vendors support lightweight integration to Identity Federation for such applications, in many cases customers will still rely on an upstream layer for authentication and authorization provided by a Web Access Management solution.
Based on our view on the market and the current demand, we opted for looking at both traditional Web Access Management and Identity Federation features in this Leadership Compass document. This view is underpinned by the fact that a number of vendors already have integrated their formerly separate offerings into a single product or at least a tightly integrated suite. Some few vendors either only support Identity Federation or still deliver two separate products. In the latter case, we have combined the separate products in our rating.



















































