1 Introduction
Identity Governance and Administration (IGA) merges the traditional User Access Provisioning (UAP) and Identity and Access Governance (IAG) markets. While many current vendors today offer comprehensive capabilities to qualify as IGA vendors, there are a few, especially the new entrants, that focus on providing either Identity Lifecycle Management (ILM) or Access Governance capabilities to meet unique requirements of the organizations.
ILM remains a core IAM requirement, but Access Governance is becoming a more sought-after capability for organizations requiring better visibility of identity administration and access entitlements across its IT infrastructure. Governance offerings range from simple reporting and dashboarding to other advanced capabilities that include AI and/or machine learning techniques enabling pattern recognition to deliver valuable intelligence for process optimization, role design, automated reviews, and anomaly detection. IGA comprises the capabilities in IAM market that broadly deal with end-to-end identity life-cycle management, access entitlements, workflow and policy management, role management, access certification, SoD risk analysis, reporting, and access intelligence and Access Intelligence for business-related insights to support effective decision making and potentially enhance governance. Several essential components and practices of IGA include:
- Identity lifecycle management
- Provisioning and deprovisioning of access
- Access intelligence
- Access request and approval
- Access certification
- Role management
- Segregation of Duties (SoD)
- Audit and compliance
The latest trend is to integrate IGA tools with AI and Machine learning (ML) capabilities. In doing so, IGA tools benefit by consuming the user's access activity such as authentication and authorization information across IT applications and systems to establish and continuously update user access patterns based on their role and peers' groups. Similarly, Data Access Governance (DAG) tools can benefit from IGA integrations by consuming user identity and access entitlement information and in turn offer contextual information on device endpoint and data residing on the device and other sources to the IGA tools for better policy management.There is a lot of scope for adoption of forecasting and prediction capabilities in IGA solutions. In the below poll result, half of the participants have not deployed AI and ML related features for supporting IGA functions. Variety of opportunities can be brought to the forefront by predicting and forecasting the outcome of activities. This function can be termed as ‘Simulations’. The opportunity to look into the future, offering a preview of what will be executed. It will help bring better insights and make better decisions. This ability to anticipate can enable organizations to prepare and strategize for potential outcomes, ensuring the avoidance of any unforeseen or undesirable consequences.
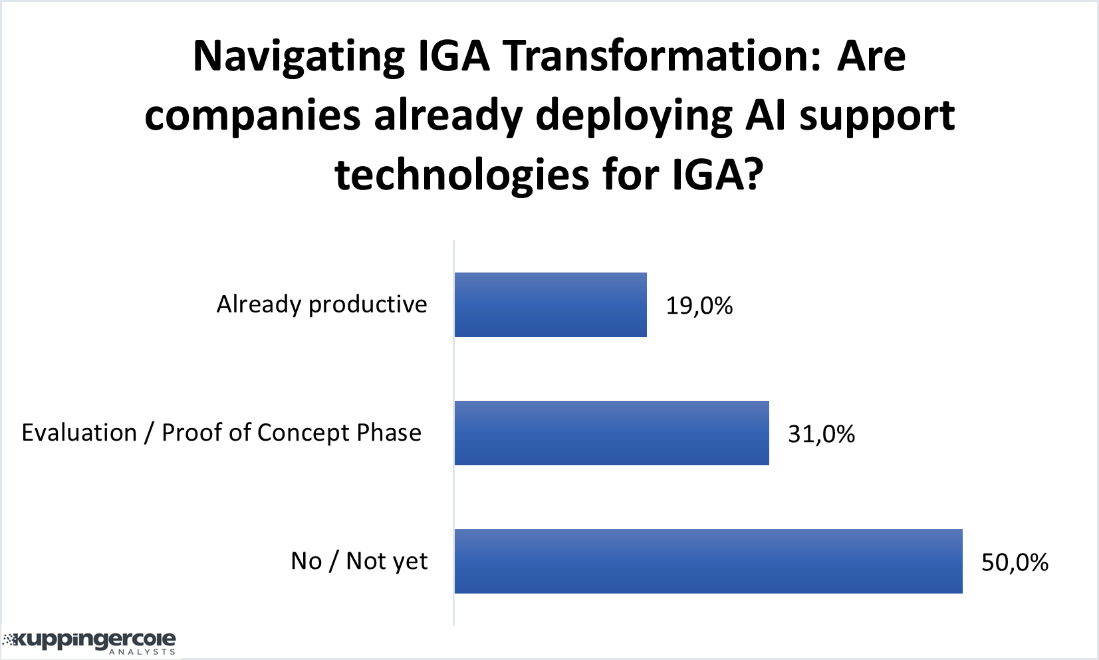
Figure 1: Scope of AI in current IGA landscape (Source: KuppingerCole Analysts)
Regarding IGA solutions, additional capabilities should be considered to improve process efficiencies, alleviate repetitive tasks, and reduce human error. Providing analytics capabilities to IGA can provide insights into access patterns, compliance status, and potential risks. The addition AI and ML can be used to automate complex tasks. Automation within IGA can help with access provisioning when new users join the organization and the deprovisioning process when users leave or change roles. Automating these processes can help minimize the risk of orphaned accounts and unauthorized or overprovisioned access. Another consideration for organizations is moving IT security services to the cloud and adopting cloud-native approaches to attain cost efficiency, scalability, agility, and innovation capabilities. Vendors have identified this opportunity of AI and ML and have started working on it to provide new capabilities. Evolveum has made investments in its IGA platform by introducing various features leveraging AI and ML.


















































