Zero Trust and KuppingerCole’s Identity Fabric 2025: A New Foundation for Secure Access
Zero Trust is a widely accepted security trend that describes a new security paradigm that focuses on identity as the new defensive parameter. With this shift towards identity, Identity and Access Management (IAM) becomes even more important, because IAM servers as a strong foundation for Zero Trust.
As the Zero Trust security model continues to gain traction across organizations, the recently updated KuppingerCole Identity Fabric and Reference Architecture both provide valuable insights into how to navigate this transformative approach. Released on January 14, the update emphasizes three core aspects that are redefining the landscape of IAM.
- Differentiation of identity types
- The importance of timely access
- Real-time analytics and actions based on dynamic access
Organizations striving to align with IAM and Zero Trust principles must address the shift from traditional, static models to dynamic, real-time, and context-aware approaches. The following insights highlight how organizations can navigate these challenges.
Figure 1: KuppingerCole Identity Fabric 2025
Identities Are Not Flat: A Growing Complexity in Identity Types
For years, identity management treated different identity types as flat, uniform entities. However, this approach is no longer sufficient. The distinction between Human Identities and Non-Human Identities (NHI) highlights how varied the challenges and requirements have become.
When it comes to Human Identities, organizations now recognize the importance of distinguishing between workforce members, B2B suppliers, B2B partners, and consumers. These groups each have distinct attributes, tasks, and access requirements. Ignoring this granularity risks oversimplification, which could lead to security gaps and operational inefficiencies.
Meanwhile, the rise of NHIs introduces even more diversity. Today, technical identities include IoT devices, operational technology (OT) devices, workloads, cloud services, agents, and bots, each playing critical roles in dynamic IT environments. Managing these identities demands not only recognition of their specific characteristics but also tailored strategies to secure their access.
This ongoing differentiation highlights a fundamental truth: Effective Zero Trust implementation begins with robust identity management that acknowledges and embraces complexity.
Figure 2: Differentiation of the identity types based on the Identity Fabric 2025
Timely Access: The New Security Benchmark
Access does not always occur within the same time-sensitive context, and security measures must account for this. Zero Trust emphasizes "just-in-time" access, guided by the principles of Least Privilege and Zero Standing Privileges.
KuppingerCole Analysts expects future IAM to operate across multiple time dimensions:
- Admin-time: Setting up access rights for users or devices in advance.
- Session initialization (real-time): Making dynamic, context-aware access decisions at the moment of login.
- Session management (real-time): Continuously monitoring and securing ongoing activity during a session.
- Post-event time: Analyzing access patterns after events for insights, compliance, and auditing.
Among these, real-time capabilities are becoming the most critical. Organizations must not only determine who can access resources but also dynamically reassess this access based on context, ensuring every action aligns with Zero Trust principles.
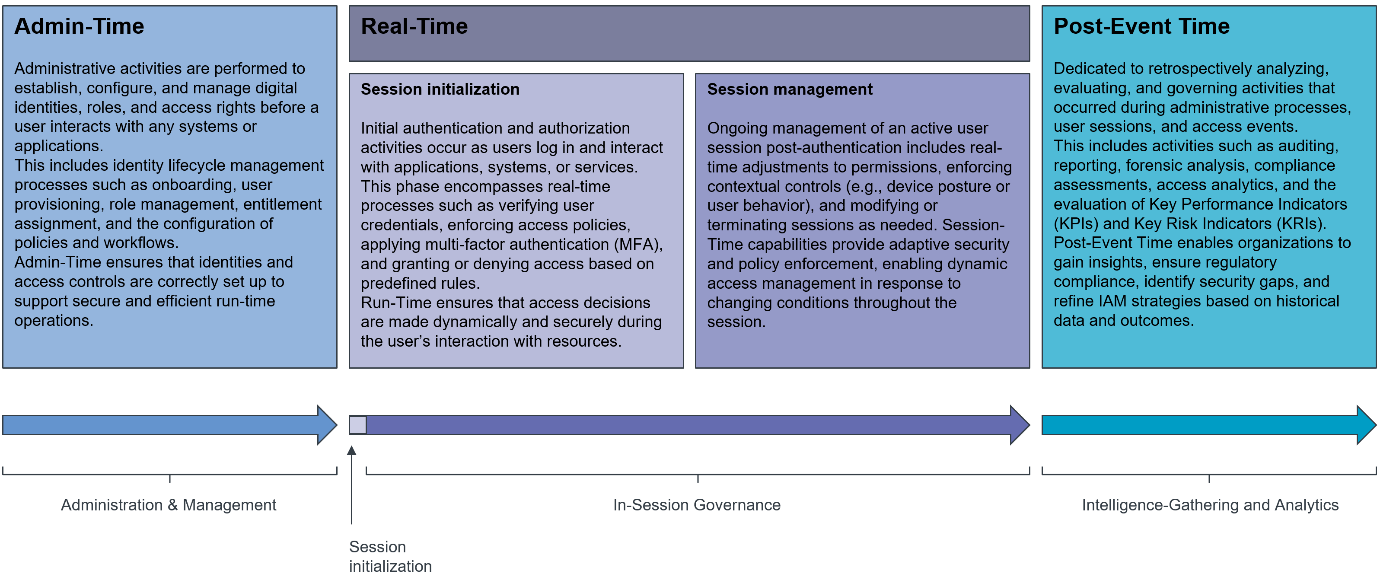 Figure 3: Dimensions of time in IAM
Figure 3: Dimensions of time in IAM
From Awareness to Action: The Role of Real-Time Analytics
Awareness of potential threats is no longer enough. Modern security demands the ability to act immediately. Continuous monitoring, enabled by real-time analytics, becomes a cornerstone of Zero Trust defense.
The ability to detect malicious behavior or anomalies in an identity's access patterns is only part of the equation. Executing defensive measures in real time represents the next step and is a significant leap forward. Analytics-driven automated decision engines enable organizations to block threats as they emerge, because knowing that an identity is behaving maliciously is only half the battle - taking immediate action is what mitigates risk.
Toward a Dynamic Zero Trust Future
The updated KuppingerCole Identity Fabric and Reference Architecture both emphasize that Zero Trust is not a static destination but a dynamic journey. Differentiating identities, embracing real-time decision-making, and leveraging analytics are no longer optional but foundational to achieving the agility and security modern organizations require.
By understanding and implementing these principles, organizations can drive forward their Zero Trust initiatives with confidence and build an IAM landscape that is both adaptive and secure.