1 Introduction
Today’s rapidly evolving digital landscape has ushered in a new era where digital technologies have profoundly transformed business operations and daily life. This digital revolution has disrupted conventional business models, creating both opportunities and challenges for organizations striving to maintain a competitive edge. One critical area that has emerged in response to these changes is governance, risk, and compliance (GRC). Effective GRC is crucial for ensuring that organizations not only comply with regulatory requirements but also manage risks and govern their operations efficiently.
Achieving robust GRC is challenging, particularly in the increasingly complex and dynamic digital environment, as well as the growing number of regulations that now, in addition to international standards like ISO27001, PCI DSS, and SOC2, also include regional regulations such as NCA Essential Cyber controls, DORA, NESA SIA, SAMA Cyber Security, and Australia’s Essential Eight Maturity Model, as well as industry-specific regulations.
Governance, risk, and compliance are essential components of an effective approach to managing an organization's overall governance structure, risk management processes, and compliance with laws, regulations, and internal policies. As organizations integrate advanced technologies and digital solutions into their operations, the need for a robust GRC framework becomes even greater. The interconnected nature of modern business operations means that any lapse in governance, risk management, or compliance can have far-reaching consequences, potentially jeopardizing an organization's reputation, financial stability, and operational continuity.
One of the main challenges organizations face in improving their GRC processes, is the manual nature of much of the work involved. Traditional GRC activities often rely heavily on manual data collection, processing, and reporting, which are not only time-consuming but are also prone to human error. These manual processes can lead to inconsistencies, inaccuracies, and delays in decision-making, making it difficult for organizations to respond swiftly to emerging risks and compliance issues. The lack of standardization in processes and procedures adds to these challenges, as different departments or regions may implement GRC activities in different ways, leading to fragmented and inefficient operations.
As data volume grows, consolidating data from various sources becomes challenging, increasing the number of hours required to validate the information manually. This can lead to inconsistencies and inaccuracies in the analysis of large datasets. Additionally, the lack of a consolidated dashboard and customizable reporting, which provides clear and easy-to-understand reports with insightful visualizations of business and technology risks, results in an incomplete and fragmented view of the organization's risk posture.
The cost of regulatory compliance failure is another significant concern for organizations. Non-compliance with industry regulations and standards can result in substantial fines, legal penalties, and damage to an organization's reputation. The financial implications of compliance failures can be devastating, particularly for heavily regulated industries such as finance, healthcare, and manufacturing. Therefore, it is imperative for organizations to establish effective GRC frameworks that minimize the risk of compliance breaches and ensure adherence to relevant laws and regulations.
In addition to the challenges posed by manual processes and compliance costs, multinational organizations must also navigate the complexities of applying GRC across different regions of the world. Global operations often involve diverse regulatory environments, with each country or region having its own set of security and privacy laws. Achieving international and regional compliance requires a keen understanding of these laws and the ability to implement controls that meet varying regulatory requirements. This task is further complicated by the need to monitor and adapt to changes in regulatory landscapes continuously, which can be resource-intensive and challenging to manage.
Another critical aspect of effective GRC is the ability to collect, analyze, and report on relevant information using different applications and tools. Organizations typically rely on a variety of software solutions to manage their GRC activities, which can lead to data silos and difficulties in consolidating information for comprehensive analysis and reporting. The challenge of integrating these disparate systems and ensuring seamless data flow is a significant one that organizations must overcome to gain a comprehensive view of their governance, risk, and compliance posture.
Reviewing hundreds of firewalls and ensuring compliant controls to maintain the separation of duties (SoD) are additional challenges that organizations may face in their GRC efforts. Firewalls are a critical component of an organization's security infrastructure, and regular reviews are necessary to ensure they are configured correctly and effectively protecting against threats. However, the sheer number of firewalls that need to be reviewed can be overwhelming, and manual reviews are often insufficient to identify all potential vulnerabilities. Similarly, ensuring that access controls are in place to maintain SoD is vital for preventing unauthorized access and reducing the risk of fraud. However, implementing and monitoring these controls across an organization can be a complex and resource-intensive process.
GRC solutions are essential for organizations to manage risks, ensure compliance, and achieve strategic objectives. While these systems have evolved significantly, they still face the following challenges in meeting the complex needs of modern businesses:
- Data Integration Difficulties: Many GRC solutions lack robust API connections, limiting integration with essential legacy or custom systems. This hinders data flow, automation, and overall efficiency.
- Manual Processes: Reliance on manual tasks for risk assessment, issue management, and reporting can be inefficient and error-prone.
- Siloed Information: Data and insights often reside in separate systems, hindering a holistic view of risks and compliance.
- Poor User Experience: Complex interfaces and limited user adoption hinder the effectiveness of the solution.
- Limited Scalability: Inability to adapt to changing business needs and growth.
- Insufficient Reporting Capabilities: Difficulty in generating actionable insights from data.
Addressing these challenges is essential for ensuring that organizations can manage risks, comply with regulations, and govern their operations efficiently, which is where automation comes in. Automation technologies, including robotic process automation (RPA) platforms, can streamline and enhance GRC processes by reducing the reliance on manual tasks, minimizing human error, and ensuring consistency (standardization) and accuracy across various operations. By leveraging RPA, organizations can automate routine and repetitive tasks such as data collection, data processing, and compliance monitoring, freeing up valuable human resources to focus on more strategic activities.
Essentially, RPA refers to the use of software robots or “bots” to automate high-volume repetitive and rule-based tasks. The bots mimic human interactions with digital systems, performing tasks such as data entry, data extraction, data validation, and transaction processing. RPA, therefore, provides a cost-effective and efficient way to automate mundane and time-consuming activities, enabling employees to focus on more value-added tasks. RPA technology is complementary to artificial intelligence (AI) in the context of automation. While RPA focuses on automating rule-based tasks, AI can apply algorithms to analyze and interpret extracted information, it can enhance the decision-making capabilities of bots, and it can enable bots to understand content and user inputs using natural language processing (NLP). AI can also be used to detect patterns, learn from data, adapt to new scenarios, and improve its own performance.
RPA platforms can play a crucial role in reducing regulatory compliance costs by automating the tracking and reporting of compliance metrics. These platforms can continuously monitor changes in regulations and automatically update compliance procedures, ensuring that organizations remain compliant without the need for extensive manual intervention. Furthermore, RPA can facilitate the integration of data from disparate systems, creating a unified view of an organization's risk and compliance posture. This comprehensive view enables more informed decision-making and enhances the organization's ability to respond swiftly to emerging risks and compliance issues.
Global regulatory environments pose a significant challenge for organizations, as they must navigate varying laws and regulations across different regions. Automation tools can be programmed to account for regional differences in compliance requirements, ensuring that GRC processes are tailored to meet local regulations. This adaptability is essential for multinational organizations operating in diverse regulatory landscapes. Additionally, RPA platforms can help in achieving international and regional compliance by automating the validation and reporting of compliance with standards such as GDPR, HIPAA, and ISO 27001, among others.
Another critical area where automation can significantly improve GRC processes is in the management of firewalls and access controls. Reviewing hundreds of firewalls manually is a daunting task prone to errors and inconsistencies. Automation tools can streamline the monitoring and compliance process according to best practices and regulatory requirements, thereby enhancing the overall security posture of the organization
Incorporating automation into GRC frameworks not only addresses current challenges but also positions organizations to better handle future regulatory and security demands. The scalability and flexibility of automation technologies allow organizations to adapt to evolving regulatory landscapes and emerging risks without the need for extensive overhauls of their GRC processes. As the digital world continues to expand and evolve, the adoption of automation in GRC will be essential for organizations aiming to manage risks effectively, ensure compliance, and govern their operations efficiently in an interconnected and rapidly changing environment.
The market for RPA-based and AI-supported GRC automation is set to grow and mature, driven by increased regulatory complexity, the growing need for robust risk management, and the fact that businesses are under constant pressure to improve operational efficiency and reduce costs. The adoption of RPA-based GRC platforms will continue to rise as more organizations recognize the benefits of automating compliance tasks. While the largest initial uptake is in banking and finance, adoption is spreading across other industries.
Implementing RPA and AI together could pose challenges in terms of integration, skills, cost, data quality, and regulatory compliance. However, with proper planning, skills training, and a clear integration strategy, these can be managed. The benefits such as improved efficiency and accuracy, scalability, and cost savings outweigh the challenges, leading to major gains. A balanced approach is key to achieving the combined benefits while avoiding the pitfalls.
KuppingerCole Analysts expects strong growth in the market for RPA-based GRC platforms, fueled by technological advancements and increasing investment in AI and automation. Market growth will help to drive innovation and more competitive pricing.
2 Product Description
ARCON is a global technology company specializing in risk control solutions. Founded in 2006, ARCON is headquartered in Houston, Texas in the US, with offices, support, and development centers around the world. Products are focused on IT security and compliance, including privileged access management (PAM), endpoint privilege management (EPM), converged identity, and automation of governance, risk, and compliance (GRC).
The ARCON drut. robotics-based integrated GRC and process automation platform is designed to address the key challenges of GRC in the modern business environment by using robotics to replicate and automate traditionally manual and time-consuming processes.
The platform enables organizations to delegate GRC tasks to bots that can work faster, longer, and more accurately than their human counterparts, improving efficiency, productivity, and compliance, while reducing cost and freeing up employees to focus on other things like root cause analysis (RCA), process improvement, innovation, and business development.
The main GRC processes include the collection of information required to manage compliance and risk, the analysis of that information to identify compliance and non-compliance, and reporting on those findings to stakeholders. Most solutions tend to automate these processes in isolation, but ARCON combines all three into a single platform.
ARCON’s drut. technology is built on an agile robotics platform to create bots for each business function. The platform’s name is derived from a Sanskrit word meaning “agility and speed” and is designed for automating data collection, visualization, and data processing to improve GRC workflows and reporting. Although RPA-based, the platform also uses AI to support some features such as proactive risk management through the application of machine learning (ML) to detect potential compliance breaches and risks early to enable timely corrective actions and enhance the customers’ ability to adapt to new compliance requirements.
The drut. platform has a pre-built risk library of more than 3500 technology and business controls mapped to more than 20 industry standards, and allows for custom uploads of “what can go wrong” scenarios. The platform’s governance structure can be customized according to customers’ needs to review and monitor the risks and controls according to the applicable standards, domains, or business processes.
The platform includes four main integrated modules for: data collection, data analytics, reporting, and case management.
Data Collection
The collector module uses customized drut. connectors for extracting GRC information from all applications, systems, and source files. The drut. collector can work with ARCON’s proprietary RPA technology to extract information from data warehouses as well as Open Database Connectivity (ODBC) and other application programming interfaces (APIs), MS Excel files, and Comma-Separated Values (CSV) files to extract information from all other sources. These can include cloud-based applications (SaaS), enterprise resource planning (ERP) reports, spreadsheets, emails, process notes, notifications, and newsletters across multiple departments in an organization. The platform also has built-in optical character recognition (OCR) for extracting information from .pdf files and unstructured data sources. The collector module also uses connectors to extract information from user authentication and access management systems, endpoint computing and enterprise management systems, network security and vulnerability management systems, and IT operations and service management systems. Information can be collected continuously or on a scheduled basis. The frequency can be set by customer organizations.
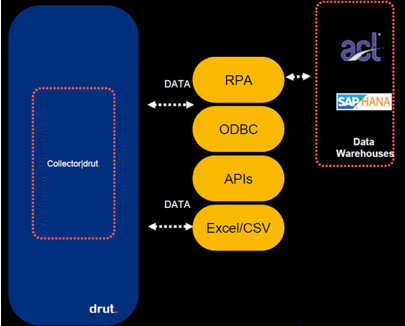
Figure 1: Collector module (source: ARCON)
Data Analytics
The analytics module has an internal data mart that is used to digest raw data, size it, and make it available for analytics and reporting to ensure a highly scalable analytics capability. The module can also run continuously or on a predefined frequency set by customer organizations. The module has a smart query builder which is a low-code/no-code solution that works using drop down menus of common search queries to generate queries in SQL to generate analytical output. No coding ability is necessary; however, the features of the analytics module can be extended using python or R for large data volume analytics.
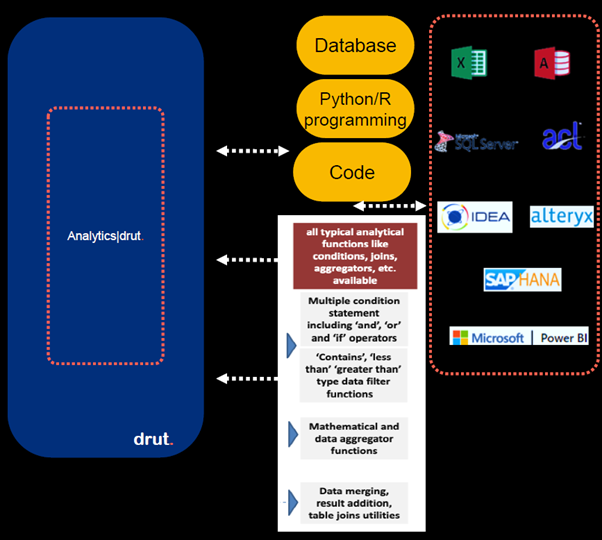
Figure 2: Analytics module (source: ARCON)
Reporting
The reporting module is designed to inform relevant stakeholders about all exceptions or non-compliances. Reports can be generated and downloaded in MS Excel, MS Word, and MS PowerPoint formats and emailed automatically to stakeholders. The reporting module also includes customizable dashboards for each IT general control (ITGC) for reporting on compliance with ITGC standards and frameworks such as COBIT, ISO27001, NIST, COSO, PCI-DSS, NESA, SAMA and MAS. Customers are able to define custom controls to map to any regulatory requirements or organizational policies.
There are two types of dashboards providing near-real-time visualization:
- Process dashboards tailored for specific control scenarios featuring metrics like base data count, deviation, and weighted risk parameters with customized widgets. Weighted risk parameters help in accurately prioritizing risks based on their potential impact, likelihood of occurrence, and other relevant factors. By assigning weights to different risk attributes, organizations can effectively allocate resources and mitigation efforts to address the most critical risks.
- CXO-level dashboards for managers to get a picture of what is happening in the organization as well as the ability to drill down to the level of individual controls.
Stakeholders can access dashboards to filter data to view the number of controls reviewed, to see incidents of non-compliance and associated risks, to see what controls have passed or failed, to see the residual risk, to see progress towards compliance over time, and to view the overall risk. The platform has a role-based access model, which means administrators can control who has access to the platform, including auditors, who can be granted “view only” access to exception reports.
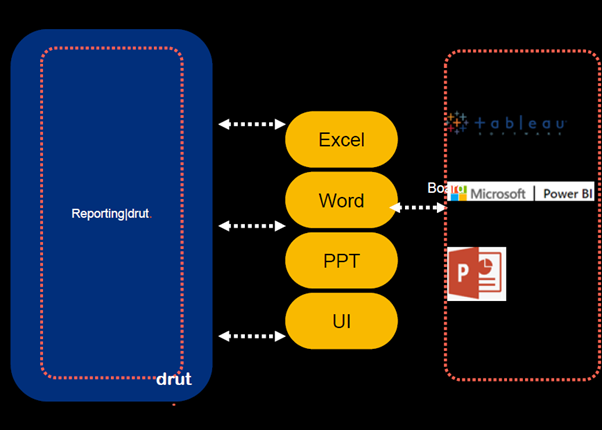
Figure 3: Reporting module (source: ARCON)
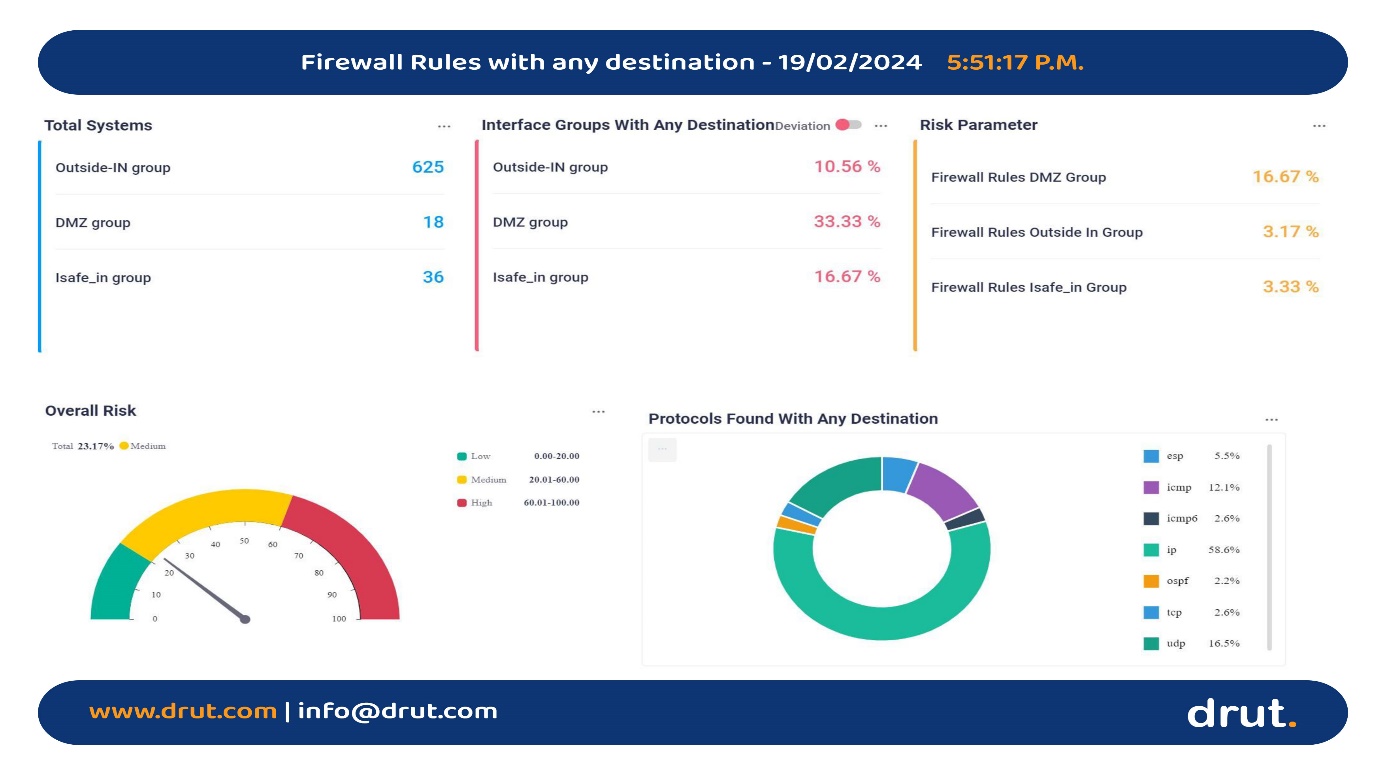
Figure 4: An example of an exception reporting screen (source: ARCON)
Case Management
The case management module is for dealing with the output of the analytics module. This built-in workflow or case management system is available for dealing with all exceptions or incidents of non-compliance. All case management goes through a three-level process, starting with the checkpoint or control owner, who can either accept exceptions and provide comments on how they should be resolved, or reject the exceptions and tag them as residual risk. The next level is the process owner, who can review and comment on the decisions of the checkpoint owner, as well as approve or reject the residual risk. The third and final level is the internal reviewer or auditor.
Process Automation
Rounding off the drut. platform’s functionality to deliver a fully unified approach to GRC automation is the ability to automate remedial actions. Once exceptions have gone through case management and remedial actions have been approved, these can be passed to process automation to carry out common GRC talks such as deactivating a user ID.
Use Cases
The wide range of use cases for robotic GRC platforms shows the versatility of these platforms in enhancing the efficiency, effectiveness, and compliance of GRC activities across any organization. Typical use cases include:
User access control reviews, which are a critical component of an organization’s security, compliance, and operational efficiency strategies. However, the complexity of modern IT environments, the volume of users and permissions, lack of standardization, susceptibility to human error, and resource-intensive nature of these reviews pose significant challenges. The drut. platform can address these challenges by automating, streamlining, and standardizing the process, ensuring that reviews are both thorough and efficient.
According to an ARCON case study, the drut. platform was able to validate more than 20 controls across more than 10,000 users. The platform enabled 100% coverage and delivered daily monitoring of end user access, ensuring only authorized users were granted access. The organization’s compliance status was also mapped to international and local regulations. ARCON claims the platform implementation and automation of user access control reviews was completed in a week.
Firewall rule reviews are another important component of security, compliance, and operational efficiency, but the complexity of modern IT environments, the volume of firewall rules, the lack of standardization, susceptibility to human error, and resource-intensive nature of these reviews pose significant challenges. The drut. platform can address these challenges by automating, streamlining, and standardizing the process, ensuring that reviews are both thorough and efficient.
According to an ARCON case study, the drut. platform was able to able to review 200,000 firewall rules across more than 200 firewalls and more than five different types of firewall in several locations to provide 100% coverage of all firewall rules. Previously the organization was able to review only a sample of 10 to 30 firewalls on a quarterly basis, which meant not all risks were known. The drut. platform was able to identify all risky rules, services, and IP addresses in use. It was also able to identify if any unwanted ports were open, if there were any unwanted sources coming into the network, and if there were any risky configurations. ARCON claims that the platform implementation and automation of the firewall rule reviews was completed in three weeks.
User access and SoD control reviews in SAP are for many organizations, especially in the retail sector, extremely important for ensuring security, compliance, and operational efficiency. However, they also present significant challenges due to the complex and dynamic nature of enterprise IT environments, the number of users and permissions, and complex role definitions. Effective access and SoD controls require continuous monitoring and regular reviews. The drut. platform can address these challenges by automating access reviews and SoD analysis, providing a unified view of user permissions across all systems, and enabling regular reviews of access controls and SoD configurations.
According to an ARCON case study, the drut. platform was able to collect data about more than 70 functions, 500 roles, and 200 custom SAP transaction codes (T Codes) associated with more than 1,500 users to review more than 150 SoD controls. The drut. platform was able to identify all policy violations and deliver 100% coverage. Previously, the organization was able to review only a sample of critical SoD cases.
Other potential use cases include:
- Automating business reporting to enhance decision-making
- Creating real-time performance dashboards
- Optimizing business operations by eliminating data inconsistencies
- Regulatory compliance management
- Vendor risk and supply chain management
- ITGC monitoring and continual testing
- Risk assessment and mitigation
- Fraud detection and prevention
- Data protection and privacy management
- Financial reporting, invoice processing, and payroll automation
- Customer service management
ARCON claims that organizations can expect around 59% reduction in cost, an 86% improvement in productivity, and a 92% improvement in compliance.
ARCON provides comprehensive training and global support services to ensure the successful implementation, adoption, and ongoing usage of the GRC Solution
3 Strengths and Challenges
ARCON’s drut. Robotics GRC Platform provides an integrated solution that delivers a unified approach to GRC automation to enable customer organizations to address the main challenges associated governance, risk, and compliance in today’s dynamic business IT environment. ARCON’s approach means that managers can benefit from AI/ML enabled continuous digital risk monitoring and compliance assessment. This means they can see current risks and identify easily where they need to focus and what processes need to be improved to minimize risk. Managers can then create and manage improvement and remediation workflows as well as automate remedial actions using RPA technology all within a single platform that can be deployed on-premises, in the cloud, or using a hybrid or robotic-process-automation-as-a-service (RPaaS) model. In addition to a base platform fee, pricing is simply based on the number of controls that customers want to monitor.
While the platform has a wide range of applications, it is still evolving and could benefit from increased use of AI capabilities. For example, although the interface is user-friendly, the addition of a chatbot or similar feature could help users to navigate the platform more easily to access the features they require. The platform would also benefit from the introduction of a mobile app or some other mobile access to keep stakeholders always informed and enable them to make informed decisions wherever they may be. As reflected by the product roadmap, ARCON is aware of these challenges and is planning to address them.
In addition to introducing mobile access to compliance reports, and introducing a chatbot feature, ARCON plans to launch a training and awareness module designed to help users to manage GRC tasks confidently. ARCON also plans to launch a technology marketplace within the GRC platform to enable easy integration with complementary technologies. The marketplace is intended to offer a selection of partner solutions and APIs to enable customers to extend the functionality of the platform to meet specific needs and new requirements as the business IT landscape changes and evolves.
ARCON’s drut. Robotics GRC Platform is ideal for large organizations with complex GRC challenges such as those in the government and public sectors, telecommunications, financial services and banking, healthcare and pharmaceutical, energy, manufacturing, retail, education, travel, and transportation. The platform will benefit organizations, especially those in highly regulated industries, looking to reduce risk and cost, while improving compliance and security through faster, more accurate and efficient GRC processes.
| Strengths |
|
| Challenges |
|
4 Related Research
Leadership Compass:: Access Control Solutions for SAP and other Business Applications
Leadership Compass: Access Control Tools for Multi-vendor LoB Environments
Leadership Comass: Access Control Tools for SAP Environments
Leadership Compass: Access Governance
Leadership Compass: Identity Governance & Administration 2022
Market Compass: Integrated Risk Management Platforms
Leadership Brief: Robotic Process Automation
Whitepaper: IAM Convergence: Integrated Perspective Beyond Just IAM
5 Copyright
© 2025 KuppingerCole Analysts AG. All rights reserved. Reproducing or distributing this publication in any form is prohibited without prior written permission. The conclusions, recommendations, and predictions in this document reflect KuppingerCole's initial views. As we gather more information and conduct deeper analysis, the positions presented here may undergo refinements or significant changes. KuppingerCole disclaims all warranties regarding the completeness, accuracy, and adequacy of this information. Although KuppingerCole research documents may discuss legal issues related to information security and technology, we do not provide legal services or advice, and our publications should not be used as such. KuppingerCole assumes no liability for errors or inadequacies in the information contained in this document. Any expressed opinion may change without notice. All product and company names are trademarks™ or registered® trademarks of their respective holders. Their use does not imply any affiliation with or endorsement by them.
KuppingerCole Analysts supports IT professionals with exceptional expertise to define IT strategies and make relevant decisions. As a leading analyst firm, KuppingerCole offers firsthand, vendor-neutral information. Our services enable you to make decisions crucial to your business with confidence and security.
Founded in 2004, KuppingerCole is a global, independent analyst organization headquartered in Europe. We specialize in providing vendor-neutral advice, expertise, thought leadership, and practical relevance in Cybersecurity, Digital Identity & IAM (Identity and Access Management), Cloud Risk and Security, and Artificial Intelligence, as well as technologies enabling Digital Transformation. We assist companies, corporate users, integrators, and software manufacturers to address both tactical and strategic challenges by making better decisions for their business success. Balancing immediate implementation with long-term viability is central to our philosophy.
For further information, please contact clients@kuppingercole.com.

















































