As organizations accelerate their cloud adoption, they face increasingly complex security challenges in multi-cloud environments. In 2025, the Chief Information Security Officer (CISO) has shifted from a reactive focus on threat mitigation to proactive leadership in safeguarding operational resilience. Addressing these challenges requires an approach centered around four foundational pillars: Shared Responsibility, Identity-Centric Security, Data Security, and Threat Resilience.
Organizations and society have become deeply dependent on digital services, amplifying the business impact of cyber threats and the necessity for cyber resilience. Recent incidents demonstrate how ransomware attacks and even mistakes can disrupt public services including healthcare.
Furthermore, the rise of machine learning (ML) and artificial intelligence (AI), particularly generative AI (GenAI), introduces both challenges and opportunities. While adversaries increasingly leverage these technologies, ML and GenAI can also enhance cyber resilience when integrated effectively into security solutions.
To survive in a world of increasing cyber threats, organizations must go beyond merely preventing these threats from impacting their digital infrastructure—they must also enhance their capabilities to respond to and recover from cyber incidents rapidly and effectively.
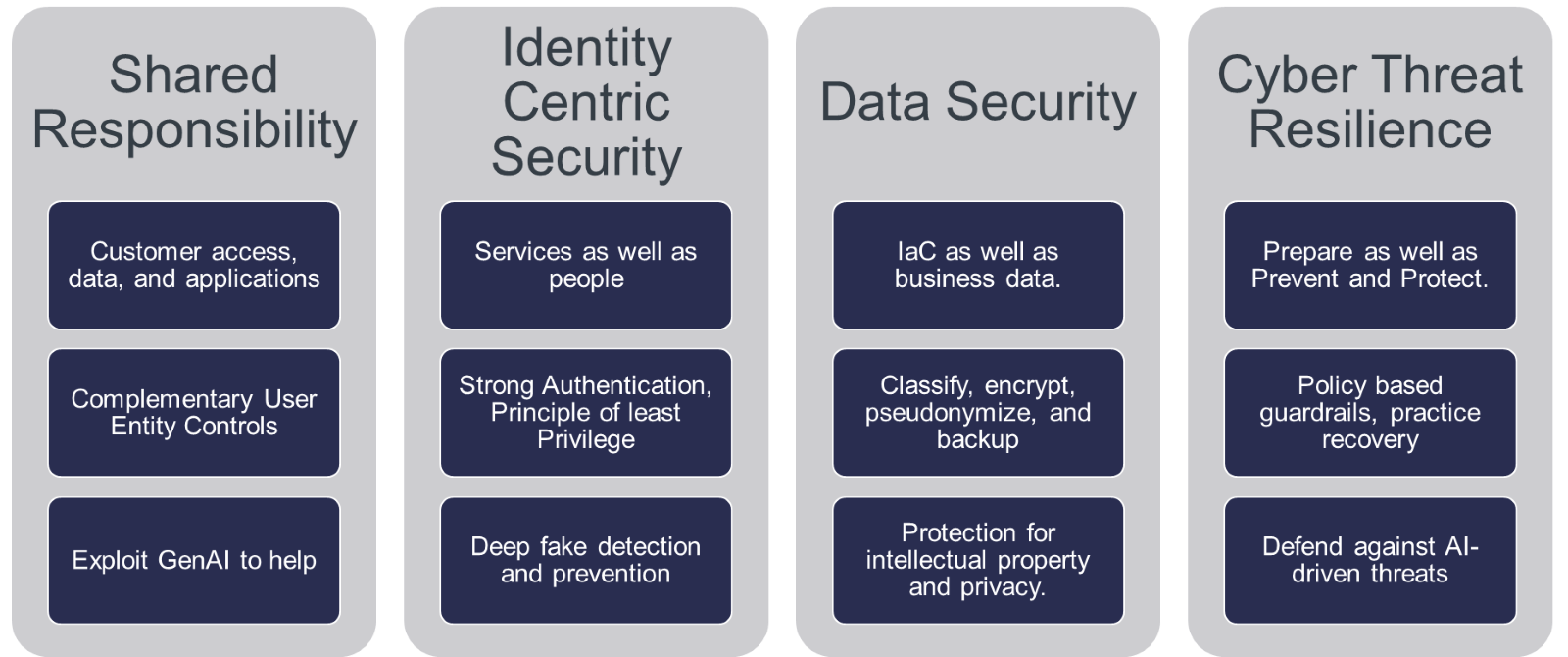
Figure 1: The 4 pillars of cloud security
Shared Responsibility: Implement Effective Controls
The shared responsibility model is fundamental to cloud security. While cloud service providers (CSPs) ensure the security of the cloud infrastructure, customers are responsible for securing the applications, data, and configurations within the cloud. Alarmingly, most cloud security incidents arise not from provider vulnerabilities but from customer misconfigurations and errors. For example, in April 2024, AT&T reported that a threat actor had exfiltrated files containing AT&T records of customer call and text interactions with their 109 million customers.
Senior security leaders must:
- Implement Controls: The cloud customer is responsible for implementing the relevant Complementary User Entity Controls (CUECs). Make sure that your organization implements these and tests their effectiveness.
- Leverage relevant tools: Utilize not only the native tools provided by CSPs, but also the new tools now on the market such as CNAPP and AISPM, to enhance visibility and automate configuration checks.
- Exploit GenAI: to help to monitor and manage shared your organization’s responsibilities more effectively.
Identity-Centric Security: Control Privileges and Always Verify
In the cloud, identity is the cyber perimeter. Ensuring that services and people have the correct entitlements to perform their roles—and no more—is critical to minimizing risk.
Key strategies include:
- Include non-human identities (NHI) – in a software defined infrastructure services as well as people need authentication and entitlements. Continuously validate trustworthiness.
- Implement strong authentication: Deploy multi-factor authentication (MFA) and biometrics for robust access control.
- Least privilege principles: Restrict access rights to what is strictly necessary. Implement privilege access management.
- Defend against deep fakes: Train staff to recognize that a video or voice does not provide proof of identity.
Data Security: Protect what matters
-
Data is at the heart of every organization, making its protection a top priority. In the cloud this includes not only the business data but also the data that defines the applications, services and infrastructure. Effective data security in the cloud involves safeguarding information in transit, at rest, and during processing, while ensuring accessibility for legitimate purposes.
Best practices involve:
- Data discovery and classification: Identify the data that your organization depends upon and implement appropriate protection policies.
- Infrastructure as Code (IaC) protection: Don’t forget to secure configuration data and deployment pipelines.
- Encryption and pseudonymization: Apply encryption methods and anonymize sensitive data. Use the technologies available to protect sensitive data while being processed. Don’t forget to plan your migration to quantum safe encryption.
- Protect GenAI training data: Protect data used for training GenAI to ensure that there is no breach of privacy or leak of intellectual property.
- Secure Backup – don’t forget to backup data as the final protection against loss.
Threat Resilience: Prepare for the Expected
A resilient organization anticipates cyber-threats and is equipped to respond effectively. It is no longer a question of if but when your organizations will be attacked. Understand your cloud security posture, monitor the latest cyber-threats, manage vulnerabilities based on risk, backup data and practice incident response. Expect the unexpected.
Critical measures include:
- AI-driven threat detection: Leverage ML and GenAI for anomaly detection and predictive analytics.
- Policy based guardrails – resources are created dynamically and scanning for vulnerabilities is not enough. You must ensure that policies control the creation of adequately secured resources.
- Incident response preparation: Develop and test cloud-specific incident response playbooks. Practice prevents poor performance when an incident occurs.
- Defend against AI-driven threats: Fortify defenses against adversarial AI and GenAI-based attacks.
Cloud Security is more than a list of acronyms
There are many cloud security products on the market including CASB, CIEM, CNAPP, CSPM, CWPP, and more. Implementing effective cloud security involves more than deploying this alphabet soup. Cloud services can provide highly resilient and cost-effective IT services but it is up to the organization to use these securely. As well as embedding security into the organizational fabric and aligning it with business objectives, CISOs must respond to the new dangers and exploit the new opportunities from GenAI.
The 4 Pillars of Cloud Security in the age of generative AI provide a practical yet strategic framework to safeguard the organization’s cloud journey. These can help organizations to navigate the complexities of cloud environments and protect against evolving cyber-threats.
To find out more about this, join us at EIC Europe's leading event for the future of digital identities and cybersecurity from May 6 - 9, 2025, in Berlin, Germany!



















































