1 Introduction
Over the past decade information technology environments have become increasingly complex as organizations grapple with accelerating technology advances and rapid migration of social mores. Organizations are increasingly seeking solutions that permit line-of-business applications to access corporate data while ensuring access is both appropriate and authorized; adhering to appropriate regulation is expected.
Smartphones are now the predominant end-user device. In the past, when a user’s access was from a PC on company premises, it was relatively easy to secure access to corporate data but now there is a requirement to manage access from coffee shops, via a highly portable device with a tendency to be lost or stolen.
AI programs with a rapacious appetite for data often use APIs to diverse applications and data repositories, adding a requirement for sophisticated key or token management to the access control task. Developers are often left to their own devices with inadequate direction on how to secure and monitor API activity; a policy-based authorization service can significantly mitigate this vulnerability.
Corporate applications increasingly reside in various hybrid environments, from on-prem applications at one end of the spectrum to containerized cloud environments on the other, all with the need to access company data. This diverse environment makes consistent access control even more difficult to achieve.
The accelerating complexity of IT environments is fueling the adoption of Authorization services, as opposed to more simple role-based access control environments. While ‘role’ is an important attribute, for instance, the Chief Financial Officer gets wider access to corporate applications than an Accounts Payable Clerk, these days a finer-grained access framework is needed. Additional personal attributes must typically be evaluated. Has a user been trained on the application they are trying to access? Is an access request coming from a user currently traveling in China? Is a user’s behavioral analysis risk score adequate for the application being accessed?
Device attributes must also be evaluated. Is the smartphone password-protected? Has the device been jailbroken? Is the corporate data container installed?
In an environment with such complexity an Authorization service is typically employed to facilitate fine-grained, context-aware, access control with centralized administration for consistent application of policy.
An outline of Symphonic’s solution is as follows:
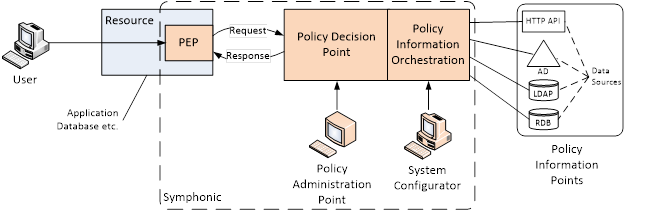
- Policy Enforcement Point
A facility to allow an application to apply the result of a request for an access control decision when a user seeks access to a protected resource. For legacy systems the PEP is a few lines of code inserted into the application but increasingly APIs are being used to request access and receive the response from the decision point. - Policy Decision Point
The core of the authorization service that queries the appropriate data sources to form an access control decision, and evaluates a request against the policies established by the business to determine the correct decision for user access to a requested resource. - Policy Information Orchestration
The facility that ensures the data returned to the decision point query is sourced from the correct repository and is combined or transformed where necessary to allow a policy to be appropriately evaluated. - Policy Information Point
Typically, one or more data repositories that contain the identity or other attributes and contextual information needed to make a decision regarding the requested access. - Policy Administration Point
The facility that allows access-control policy to be defined. The UI must accommodate the intended user-base, for technical staff a programming interface is typically used, for a business user a natural language expression builder is more appropriate.
The way in which these components support the requirements of the relying applications is critical to the success of an authorization service. The “Trust Framework” for each Symphonic deployment is configured to the client’s environment. Symphonic provide interfaces to attribute repositories and credential stores, and integration packages for specific industry risk-scoring services are also offered.

















































