1 Introduction
The KuppingerCole Leadership Compass provides an overview of vendors and their product or service offerings in a certain market segment. This Leadership compass focuses on the market segment of CASBs (Cloud Access Security Brokers). CASBs address the challenges of security and compliance around the use of cloud services. They provide security controls that are not available through existing security devices and provide a point of control over access to cloud services by any user and from any device. The market for CASBs has evolved from the first products that focussed on the discovery of cloud usage, through network access control points to become integrated cloud security solutions. These are sometimes called CASB+ or CASB 2.0.
1.1 Market Segment
Most organizations are now using several cloud services as well as on-premises and hosted IT services. This hybrid environment has given rise to many challenges in the areas of management, security, and compliance. This is because the use of these services is not well integrated into the normal IT and access governance processes and technologies found within organizations. Furthermore, the use of these services create other risks.
Employees and associates can use their personal cloud services to perform their jobs without reference to their employer. Line of business managers can acquire cloud services without performing risk assessment or considering the impact of these on compliance. The requirements for control over the processing and storage of personal data from the recent EU GDPR is one example of these challenges. The uncontrolled use of cloud services also increases cyber-risks; cyber adversaries may obtain unauthorized access to steal or corrupt data held in the services, as well as to plant malware that could then infect the organization using them.
In an ideal world, the functionality to manage access to cloud services and to control the data that they hold would be integrated with the normal access governance and cyber security tools used by organizations. However, these tools were slow to develop the required capabilities, and this has led to a market in CASBs (Cloud Access Security brokers) to plug the gap. It is notable that some of the CASBs on the market have already been acquired by major security software vendors and are being integrated into their toolsets.
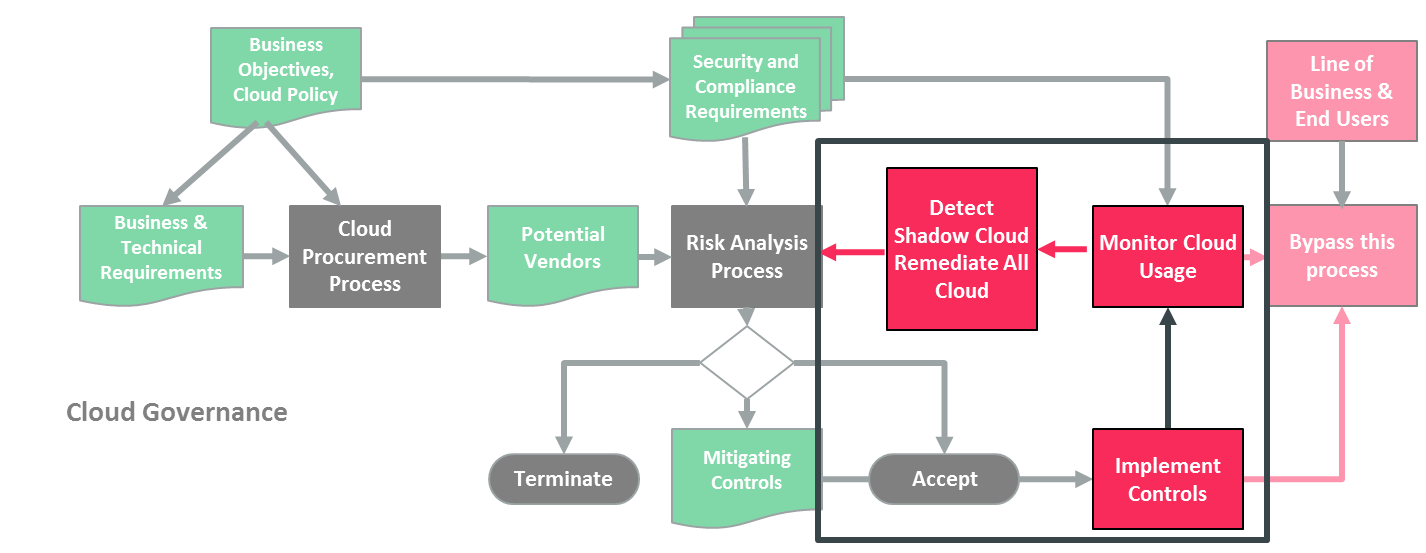
Figure 1 illustrates how CASBs fit into the overall cloud governance process. The basic functionalities that CASBs provide are:
- Discovery of what cloud services are being used, by whom and for what data.
- Control over who can use which services and what data can be transferred.
- Protection of data in the cloud against unauthorized access and leakage as well as cyber threats.
The products which address various aspects of this provide overlapping functionality and these solutions include:
- Rights Management – that provide granular access control over access to unstructured files.
- Data Leakage Prevention – that provide discovery and control over the sharing, transmission, and storage in the cloud of specific classes of data.
- Secure Web Gateways – that protect web-surfing devices from infection and enforce company policies.
- Cloud Access Security Brokers – that provide granular access over who can access cloud services and the functions that they can perform.
| Dicovery | Control | Protection | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rights Management | Sometimes include rules to detect specific kinds of data | Over individual access to unstructured files | Against unauthorized access to files including if forwarded or leaked |
| Data Leakage Prevention | Of specific kinds of data stored or being transmitted | Warn, report, quarantine, remove data, prevent transmission | Against unauthorized storage and transmission of specific types of data |
| Secure Web Gateway | Access to URLs | Over which services (URLs) can be accessed and malware filtering | Protect web-surfing devices from infection and enforce company policies |
| Cloud Access Security Broker | Who is accessing which cloud services | Granular control over who can access which transactions from where using which device | Against unauthorized access to specific services, transactions, and data |
| Access Governance | Of user, roles and entitlements | Over entitlements against policies and separation of duties | Enforcement of allocation of entitlements that are against policies and separation of duties |
The distinction between these types of product and the functionalities provided by Cloud Access Security Brokers are shown in the table. The next generation CASB 2 or CASB+ solutions now on the market providing several of these functions, sometimes through inbuilt capabilities and sometimes through integration with other products.
There are two basic discovery and control models used by CASB+ solutions: network-based control (using a proxy for example) and cloud-service-based control (using cloud service APIs). Each of these approaches has advantages and disadvantages. The better solutions use a combination of the two.
However, the integration of CASBs with the traditional security products is not enough. CASBs should become more integrated with identity and access technologies over time. There is already a level of integration between most CASBs and user directories and IDaaS to identify users and feedback to enable or disable access via these. Access to cloud services and the ability to upload/download content should ultimately be governed through the same processes as access to other kinds of services.


















































